
Written by: Alex Gray, President Sightline Building Solution
Part 4 Efficient and Reliable Heating Systems for Northern Housing
This blog is part of a 12-part series exploring the challenges and solutions for building in northern and remote communities. Each installment focuses on a crucial aspect of northern housing, providing insights and best practices to create durable, energy-efficient, and resilient homes.
In our previous blog, we explored ventilation strategies essential for maintaining indoor air quality in northern homes. Now, we turn our attention to one of the most critical aspects of northern housing: heating systems. In extreme cold climates, an efficient and reliable heating system is not just a matter of comfort—it’s a necessity for survival. Selecting the right heating solution is crucial for energy efficiency, sustainability, and long-term affordability.
Understanding Heating Challenges in the North
Heating a home in a northern climate comes with unique challenges, including:
- Extreme Cold: Temperatures can drop significantly below freezing for extended periods, increasing heating demands.
- Limited Fuel Availability: Remote communities often face supply chain difficulties, making fuel access unreliable and expensive.
- High Energy Costs: Electricity and fuel prices tend to be higher in remote areas, making energy efficiency a priority.
- Power Outages: Harsh weather conditions can cause disruptions in power supply, requiring backup heating solutions.
- Moisture and Condensation Issues: Improper heating can lead to condensation, mold growth, and damage to building materials.
Selecting the Right Heating System
The best heating system for a northern home depends on local fuel availability, infrastructure, and efficiency. Here are some of the most effective heating options:


- Wood and Pellet Stoves
Wood and pellet stoves have been used for generations in northern climates due to their reliability and accessibility.
- Pros:
- Works independently of electrical power.
- Can use locally sourced firewood, reducing fuel transportation costs.
- Provides radiant heat, which is effective in warming living spaces quickly.
- Cons:
- Requires regular maintenance and cleaning.
- Proper ventilation and chimney systems are essential to avoid air quality issues.
- Firewood collection and storage require effort and space.
- Oil and Propane Heating Systems
Many northern homes rely on oil or propane furnaces and boilers due to their ability to provide consistent and powerful heating.
- Pros:
- Efficient at heating large spaces.
- Works well in extremely cold temperatures.
- Can be connected to a thermostat for automated control.
- Cons:
- Fuel costs can fluctuate and are often high in remote areas.
- Requires a well-maintained storage tank and fuel delivery system.
- Risk of fuel spills and environmental concerns.
- Electric Heating
Electric baseboard heaters, heat pumps, and forced-air systems are common in regions where electricity is stable and relatively affordable.
- Pros:
- Low maintenance and easy to install.
- No on-site fuel storage required.
- Can be powered by renewable sources like hydro or solar.
- Cons:
- Expensive to operate in areas with high electricity costs.
- Dependent on a reliable electrical grid.
- Less effective in extremely cold temperatures compared to fuel-based heating.
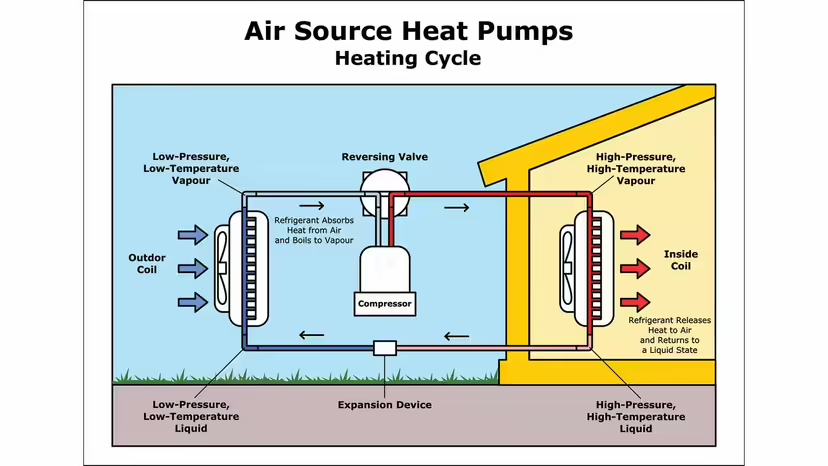
- Heat Pumps (Air Source and Ground Source)
Heat pumps extract heat from the air or ground and can be an efficient heating solution in milder northern climates.
- Pros:
- Highly efficient and can reduce energy costs over time.
- Can provide both heating and cooling.
- Works well with renewable energy sources.
- Cons:
- Air-source heat pumps lose efficiency in extreme cold.
- Ground-source heat pumps require significant upfront installation costs.
- Needs electricity to operate, making power outages a concern.
- District Heating and Biomass Systems
Some northern communities are investing in district heating systems, where a centralized heating plant distributes heat to multiple buildings.
- Pros:
- Can use local biomass (wood chips, pellets) to reduce fuel costs.
- More efficient than individual heating units.
- Reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- Cons:
- Requires community-wide infrastructure investment.
- Needs proper management and maintenance.
Energy Efficiency Strategies for Heating
Regardless of the heating system used, efficiency measures can significantly reduce heating costs and energy consumption:
- Proper Insulation and Air Sealing
- Use high R-value insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors to reduce heat loss.
- Seal air leaks around windows, doors, and vents to prevent drafts.
- Consider triple-glazed windows for better heat retention.
- Smart Thermostats and Zoning
- Install programmable thermostats to optimize heating schedules and reduce unnecessary energy use.
- Use zone heating to focus warmth in occupied areas while reducing heat in unused spaces.
- Passive Solar Heating
- Position windows to maximize sunlight exposure during winter.
- Use thermal mass materials (e.g., stone, concrete) to store heat and release it slowly.
- Install reflective barriers to direct heat where needed.
- Regular Maintenance and System Upgrades
- Clean and inspect heating systems regularly to ensure efficiency.
- Replace outdated or inefficient units with modern, high-efficiency models.
- Upgrade insulation and ductwork to improve heat distribution.
Emergency and Backup Heating Solutions
Given the risk of power outages and extreme cold snaps, having a backup heating plan is essential:
- Wood or Pellet Stove: Provides an off-grid heating option in case of power loss.
- Battery Backup for Electric Systems: Helps maintain heating during short-term outages.
- Portable Propane Heaters: Can provide temporary emergency heating but require proper ventilation.
- Generator: A backup generator can power electric heating systems during blackouts.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right heating system for a northern home is a balance of reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Whether using wood, oil, electricity, or modern heat pumps, ensuring proper installation and maintenance is key to long-term performance.
In the next installment of our 12-part blog series on building in the North, we will explore reliable electrical systems—a crucial topic for ensuring safe and efficient electrical systems in cold climates. Stay tuned for more insights into constructing durable, energy-efficient, and sustainable homes in northern communities.
June 8, 2025
